How To Check Ppi In Photoshop
- Photoshop User Guide
- Introduction to Photoshop
- Dream it. Go far.
- What'due south new in Photoshop
- Edit your kickoff photograph
- Create documents
- Photoshop | Common Questions
- Photoshop system requirements
- Migrate presets, deportment, and settings
- Get to know Photoshop
- Photoshop and Adobe services
- Photoshop and Adobe Stock
- Artistic Cloud Libraries
- Artistic Cloud Libraries in Photoshop
- Apply the Touch on Bar with Photoshop
- Piece of work with Illustrator artwork in Photoshop
- Employ the Capture in-app extension in Photoshop
- Grid and guides
- Creating actions
- Undo and history
- Default keyboard shortcuts
- Affect capabilities and customizable workspaces
- Photoshop on the iPad
- Photoshop on the iPad | Common questions
- Get to know the workspace
- Organization requirements | Photoshop on the iPad
- Create, open, and export documents
- Add photos
- Work with layers
- Draw and paint with brushes
- Make selections and add together masks
- Retouch your composites
- Work with adjustment layers
- Adjust the tonality of your composite with Curves
- Apply transform operations
- Ingather and rotate your composites
- Rotate, pan, zoom, and reset the canvass
- Work with Type layers
- Work with Photoshop and Lightroom
- Go missing fonts in Photoshop on the iPad
- Japanese Text in Photoshop on the iPad
- Manage app settings
- Bear upon shortcuts and gestures
- Keyboard shortcuts
- Edit your prototype size
- Livestream as you lot create in Photoshop on the iPad
- Right imperfections with the Healing Brush
- Create brushes in Capture and use them in Photoshop
- Work with Photographic camera Raw files
- Create and work with Smart Objects
- Adjust exposure in your images with Dodge and Burn down
- Photoshop on the web beta
- Common questions | Photoshop on the web beta
- Introduction to the workspace
- System requirements | Photoshop on the web beta
- Keyboard shortcuts | Photoshop on the web beta
- Supported file types | Photoshop on the web beta
- Open and work with cloud documents
- Collaborate with stakeholders
- Use limited edits to your cloud documents
- Deject documents
- Photoshop deject documents | Common questions
- Photoshop cloud documents | Workflow questions
- Manage and work with cloud documents in Photoshop
- Upgrade cloud storage for Photoshop
- Unable to create or relieve a deject document
- Solve Photoshop deject document errors
- Collect cloud document sync logs
- Share access and edit your cloud documents
- Share files and comment in-app
- Workspace
- Workspace basics
- Create documents
- Use the Bear on Bar with Photoshop
- Microsoft Dial back up in Photoshop
- Tool galleries
- Performance preferences
- Utilise tools
- Touch gestures
- Touch capabilities and customizable workspaces
- Technology previews
- Metadata and notes
- Quickly share your creations
- Place Photoshop images in other applications
- Preferences
- Default keyboard shortcuts
- Rulers
- Show or hide not-printing Extras
- Specify columns for an paradigm
- Disengage and history
- Panels and menus
- Place files
- Position elements with snapping
- Position with the Ruler tool
- Presets
- Customize keyboard shortcuts
- Grid and guides
- Web, screen, and app pattern
- Photoshop for design
- Artboards
- Device Preview
- Re-create CSS from layers
- Piece web pages
- HTML options for slices
- Change piece layout
- Work with web graphics
- Create web photo galleries
- Image and colour nuts
- How to resize images
- Work with raster and vector images
- Image size and resolution
- Acquire images from cameras and scanners
- Create, open up, and import images
- View images
- Invalid JPEG Marker error | Opening images
- Viewing multiple images
- Customize color pickers and swatches
- High dynamic range images
- Lucifer colors in your epitome
- Convert between colour modes
- Colour modes
- Erase parts of an epitome
- Blending modes
- Cull colors
- Customize indexed color tables
- Image data
- Distort filters are unavailable
- About color
- Colour and monochrome adjustments using channels
- Choose colors in the Color and Swatches panels
- Sample
- Colour style or Paradigm mode
- Colour cast
- Add a conditional mode modify to an activeness
- Add together swatches from HTML CSS and SVG
- Bit depth and preferences
- Layers
- Layer basics
- Nondestructive editing
- Create and manage layers and groups
- Select, group, and link layers
- Identify images into frames
- Layer opacity and blending
- Mask layers
- Apply Smart Filters
- Layer comps
- Movement, stack, and lock layers
- Mask layers with vector masks
- Manage layers and groups
- Layer furnishings and styles
- Edit layer masks
- Extract avails
- Reveal layers with clipping masks
- Generate image assets from layers
- Piece of work with Smart Objects
- Blending modes
- Combine multiple images into a group portrait
- Combine images with Auto-Blend Layers
- Align and distribute layers
- Copy CSS from layers
- Load selections from a layer or layer mask's boundaries
- Knockout to reveal content from other layers
- Layer
- Flattening
- Composite
- Background
- Selections
- Select and Mask workspace
- Brand quick selections
- Get started with selections
- Select with the marquee tools
- Select with the lasso tools
- Select a color range in an image
- Conform pixel selections
- Convert between paths and selection borders
- Channel nuts
- Move, re-create, and delete selected pixels
- Create a temporary quick mask
- Save selections and alpha aqueduct masks
- Select the image areas in focus
- Indistinguishable, split, and merge channels
- Channel calculations
- Selection
- Bounding box
- Prototype adjustments
- Perspective warp
- Reduce camera milkshake blurring
- Healing brush examples
- Export color lookup tables
- Adjust paradigm sharpness and blur
- Understand color adjustments
- Apply a Brightness/Contrast adjustment
- Adjust shadow and highlight detail
- Levels adjustment
- Adjust hue and saturation
- Adjust vibrance
- Arrange color saturation in image areas
- Brand quick tonal adjustments
- Apply special color effects to images
- Enhance your image with color balance adjustments
- High dynamic range images
- View histograms and pixel values
- Match colors in your epitome
- How to ingather and straighten photos
- Convert a color image to black and white
- Adjustment and fill layers
- Curves aligning
- Blending modes
- Target images for press
- Adjust color and tone with Levels and Curves eyedroppers
- Adjust HDR exposure and toning
- Filter
- Mistiness
- Dodge or burn image areas
- Make selective colour adjustments
- Replace object colors
- Adobe Camera Raw
- Camera Raw organisation requirements
- What's new in Camera Raw
- Introduction to Camera Raw
- Create panoramas
- Supported lenses
- Vignette, grain, and dehaze effects in Photographic camera Raw
- Default keyboard shortcuts
- Automated perspective correction in Camera Raw
- How to make non-destructive edits in Camera Raw
- Radial Filter in Camera Raw
- Manage Camera Raw settings
- Open up, procedure, and save images in Photographic camera Raw
- Repair images with the Enhanced Spot Removal tool in Camera Raw
- Rotate, crop, and adjust images
- Adjust color rendering in Camera Raw
- Characteristic summary | Adobe Camera Raw | 2018 releases
- New features summary
- Procedure versions in Camera Raw
- Brand local adjustments in Camera Raw
- Prototype repair and restoration
- Remove objects from your photos with Content-Enlightened Fill
- Content-Aware Patch and Move
- Retouch and repair photos
- Right image baloney and noise
- Basic troubleshooting steps to ready well-nigh problems
- Image transformations
- Transform objects
- Adjust crop, rotation, and canvas size
- How to crop and straighten photos
- Create and edit panoramic images
- Warp images, shapes, and paths
- Vanishing Bespeak
- Employ the Liquify filter
- Content-aware scaling
- Transform images, shapes, and paths
- Warp
- Transform
- Panorama
- Drawing and painting
- Pigment symmetrical patterns
- Describe rectangles and modify stroke options
- Virtually cartoon
- Draw and edit shapes
- Painting tools
- Create and modify brushes
- Blending modes
- Add color to paths
- Edit paths
- Paint with the Mixer Brush
- Castor presets
- Gradients
- Slope interpolation
- Fill and stroke selections, layers, and paths
- Draw with the Pen tools
- Create patterns
- Generate a pattern using the Pattern Maker
- Manage paths
- Manage pattern libraries and presets
- Depict or pigment with a graphics tablet
- Create textured brushes
- Add together dynamic elements to brushes
- Slope
- Pigment stylized strokes with the Art History Brush
- Paint with a blueprint
- Sync presets on multiple devices
- Text
- Work with OpenType SVG fonts
- Format characters
- Format paragraphs
- How to create type effects
- Edit text
- Line and grapheme spacing
- Standard arabic and Hebrew type
- Fonts
- Troubleshoot fonts
- Asian blazon
- Create type
- Text Engine mistake using Type tool in Photoshop | Windows 8
- World-Prepare composer for Asian Scripts
- How to add and edit the text in Photoshop
- Video and animation
- Video editing in Photoshop
- Edit video and animation layers
- Video and animation overview
- Preview video and animations
- Paint frames in video layers
- Import video files and image sequences
- Create frame animations
- Artistic Cloud 3D Animation (Preview)
- Create timeline animations
- Create images for video
- Filters and effects
- Employ the Liquify filter
- Apply the Mistiness Gallery
- Filter nuts
- Filter effects reference
- Add together Lighting Effects
- Utilise the Adaptive Wide Bending filter
- Use the Oil Paint filter
- Layer effects and styles
- Apply specific filters
- Smudge paradigm areas
- Saving and exporting
- Relieve your files in Photoshop
- Export your files in Photoshop
- Supported file formats
- Save files in graphics formats
- Movement designs between Photoshop and Illustrator
- Salvage and export video and animations
- Save PDF files
- Digimarc copyright protection
- Relieve your files in Photoshop
- Printing
- Impress 3D objects
- Print from Photoshop
- Print with color management
- Contact Sheets and PDF Presentations
- Print photos in a picture package layout
- Print spot colors
- Duotones
- Print images to a commercial press press
- Meliorate color prints from Photoshop
- Troubleshoot printing bug | Photoshop
- Automation
- Creating deportment
- Create data-driven graphics
- Scripting
- Process a batch of files
- Play and manage deportment
- Add conditional actions
- Near actions and the Actions panel
- Record tools in deportment
- Add a conditional manner alter to an action
- Photoshop UI toolkit for plug-ins and scripts
- Color Direction
- Understanding color direction
- Keeping colors consistent
- Color settings
- Work with color profiles
- Colour-managing documents for online viewing
- Color-managing documents when press
- Color-managing imported images
- Proofing colors
- Content actuality
- Learn near content credentials
- Identity and provenance for NFTs
- Connect accounts for artistic attribution
- 3D and technical imaging
- Photoshop 3D | Common questions effectually discontinued 3D features
- Creative Deject 3D Blitheness (Preview)
- Print 3D objects
- 3D painting
- 3D panel enhancements | Photoshop
- Essential 3D concepts and tools
- 3D rendering and saving
- Create 3D objects and animations
- Epitome stacks
- 3D workflow
- Measurement
- DICOM files
- Photoshop and MATLAB
- Count objects in an paradigm
- Combine and catechumen 3D objects
- 3D texture editing
- Conform HDR exposure and toning
- 3D panel settings
Click any of these topics to acquire more virtually the different aspects of image size and resolution:
Printed epitome resolution
Dimensions are the total number of pixels forth the width and height of an paradigm.
Resolution is the number of prototype pixels assigned to each inch when an image is printed - measured in pixels per inch (ppi). Thus, the more pixels an image has per inch, the greater will be its resolution. And, a high-resolution image volition produce a better quality printed output.
When changing the Dimensions or Resolution, think that the image data remains abiding until you lot resample it. If you lot change the resolution, the width and pinnacle will change accordingly to maintain the same amount of image information.
Note the human relationship between Image Size and Resolution in the Prototype Size dialog box.
To navigate to the Image Size dialog box, follow these steps:
-
Go to Epitome > Prototype Size.

Navigate to the Image Size dialog box -
The Resample option checkbox is checked by default. Use information technology to adjust the dimensions of your paradigm.

Image Size dialog box in Photoshop TheParadigm Size dialog box displays the many interpolation options that you lot tin use to brand images wait well-baked and sharp even after enlarging them.
To your left is the preview window which displays a live preview of what the epitome will look similar based on the called settings. To your right are the settings themselves.
To learn more than aboutResample selection checkbox, go to its detailed description. You tin also get through the following table:
| Don't check the Resample option | Check the Resample option |
| If you lot uncheck the Resample option, you will be able to resize or change the resolution of the image by redistributing existing pixels | The Resample option is checked by default, which means yous can adjust the dimensions of the paradigm past adding or taking away pixels from the Width and Height |
You tin can adjust the Width and Height of your image in two ways - either in pixels for images to exist used online or in inches (or centimeters) for images to be printed.
Click the link icon to highlight it and preserve proportions, which volition aid you automatically suit the height when changing the width.If you lot do non click the link to preserve proportions, you will get a alpine, sparse or short, broad image that looks stretched when changing one dimension.
Learn more most the different interpolation methods by referring to Resampling.

Choose theAutomatic option, which will aid you with default interpolation. For more refined control, you can opt for the other options too. Each ane of these options is designed for specific image enlargement or reduction workflows.


To chop-chop display the current prototype size, use the information box at the bottom of the document window.
Then yous can position the mouse over the file information box and hold downwardly the mouse left button.
Monitor resolution
Monitor resolution is measured in pixels. If the resolution of the monitor and pixel dimensions of the image are the same size, the prototype volition fill the screen when viewed at 100%.
Factors that decide how large an paradigm appears on screen
- Pixel dimensions of your image
- Size and resolution settings of your monitor
In Photoshop, you lot can alter the onscreen prototype magnification, and then yous can hands piece of work with images of any pixel dimensions.
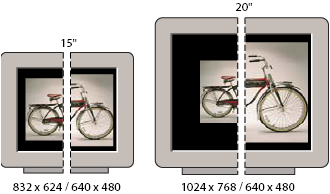
When preparing images for onscreen viewing, you should consider the lowest monitor resolution that your photograph is probable to be viewed on.
File size
The file size of an image is the digital size of the epitome file, measured in kilobytes (K), megabytes (MB), or gigabytes (GB). File size is proportional to the pixel dimensions of the image. Images with more than pixels may produce more than particular at a given printed size, simply they require more deejay infinite to store and may be slower to edit and impress. Image resolution thus becomes a compromise between image quality (capturing all the data you lot demand) and file size.
Another factor that affects file size is file format. Because of the varying compression methods used by GIF, JPEG, PNG, and TIFF file formats, file sizes tin vary considerably for the same pixel dimensions. Similarly, colour flake-depth and the number of layers and channels in an epitome affect file size.
Photoshop supports maximum pixel dimension of 300,000 by 300,000 pixels per image. This brake places limits on the print size and resolution available to an image.
Printer resolution
Printer resolution is measured in dots per inch (dpi). The higher the dpi, the finer the printed output yous'll get. Nigh inkjet printers accept a resolution of approximately 720 to 2880 dpi.
Printer resolution is different from, simply related to, image resolution. To print a high-quality photo on an inkjet printer, an image resolution of at to the lowest degree 220 ppi should provide practiced results.
Screen frequency is the number of printer dots or halftone cells per inch used to print grayscale images or color separations. Also known as screen ruling or line screen, screen frequency is measured in lines per inch (lpi), or lines of cells per inch in a halftone screen. The higher the resolution of the output device, the finer screen ruling you lot can utilize.
The relationship between prototype resolution and screen frequency determines the quality of item in the printed image. To produce a halftone epitome of the highest quality, you by and large use an image resolution that is about 1.5 to 2 times the screen frequency.
With some images and output devices, a lower resolution tin can produce good results. To decide your printer'southward screen frequency, cheque your printer documentation or consult your service provider.
Some imagesetters and 600‑dpi laser printers apply screening technologies other than halftoning. If you are printing an image on a nonhalftone printer, consult your service provider or your printer documentation for the recommended prototype resolutions.

A. 65 lpi: Coarse screen typically used to print newsletters and grocery couponsB. 85 lpi: Average screen typically used to print newspapersC. 133 lpi: Loftier-quality screen typically used to print four-colour magazinesD. 177 lpi: Very fine screen typically used for annual reports and images in art books
Resolution specs for press images
A resolution of 300 pixels/inch is the industry standard for loftier-quality prints. This resolution will ensure that your image looks sharp and detailed when printed.
A resolution of 300 pixels/inch is perfect for viewing pocket-sized prints from up shut, only y'all tin also opt for lower resolutions for large prints if they are intended to be viewed from far away. For example, if you are printing a billboard to be erected off a highway, you can impress information technology at a lower resolution without compromising on the quality, because high resolution becomes less important every bit yous motility further from the image.
Default resolution in printers
Usually, printers accept their default impress resolution at 300 pixels/inch, and if you print an image with a lower resolution, they volition adjust their image settings to print your epitome at the default resolution.
This means, you cannot print an paradigm at less than the printer's default resolution, and if you don't enlarge the image, your printer will.
View the print size onscreen
You can practise either of the following to view the print size onscreen - either grando to View > Impress Size . Or, select the Hand tool or Zoom tool and click Impress Size in the options bar.
The epitome is redisplayed in its judge printed size, every bit specified in the Document Size surface area of theImage Size dialog box. The size and resolution of your monitor affect the onscreen impress size.
Resampling
Resampling is changing the amount of image data every bit you lot change either the pixel dimensions or the resolution of an image.
Downsampling is decreasing the number of pixels - when you downsample, data is deleted from the image.
Upsampling is increasing the number of pixels - when you upsample, new pixels are added.
You specify an interpolation method to decide how pixels are added or deleted.
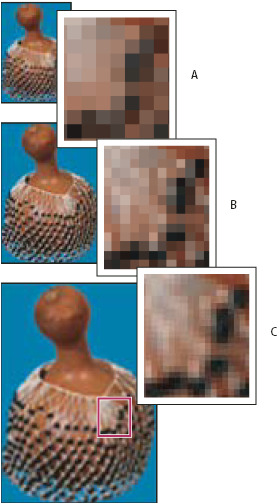
A. DownsampledB. OriginalC. Resampled upward (selected pixels displayed for each ready of images)
Keep in mind that resampling tin can consequence in poorer image quality. For example, when you resample an image to larger pixel dimensions, the image loses some item and sharpness. Applying the Unsharp Mask filter to a resampled paradigm can help refocus the epitome details.
You can avoid the need for resampling by scanning or creating the image at a sufficiently high resolution. If you desire to preview the effects of irresolute pixel dimensions onscreen or to impress proofs at unlike resolutions, resample a duplicate of your file.
Photoshop resamples images using an interpolation method to assign colour values to whatever new pixels based on the colour values of existing pixels. You can choose your method in the Image Size dialog box.
- Nearest Neighbor A fast just less precise method that replicates the pixels in an image. This method is for employ with illustrations containing edges that are not anti-aliased, to preserve hard edges and produce a smaller file. However, this method tin produce jagged effects, which become apparent when you distort or scale an image or perform multiple manipulations on a pick.
- Bilinear A method that adds pixels past averaging the colour values of surrounding pixels. It produces medium-quality results.
- Bicubic A slower simply more precise method based on an exam of the values of surrounding pixels. Using more than complex calculations, Bicubic produces smoother tonal gradations than Nearest Neighbor or Bilinear.
- Bicubic Smoother A practiced method for enlarging images based on Bicubic interpolation but designed to produce smoother results.
- Bicubic Sharper A good method for reducing the size of an image based on Bicubic interpolation with enhanced sharpening. This method maintains the item in a resampled image. If Bicubic Sharper oversharpens some areas of an image, try using Bicubic.
You can specify a default interpolation method to use whenever Photoshop resamples image data. Choose Edit > Preferences > General (Windows) or Photoshop > Preferences > Full general (MacOS), and then cull a method from the Paradigm Interpolation Methods menu.
Change pixel dimensions of an epitome
Changing an image's pixel dimensions affects not only its onscreen size only also its image quality and its printed characteristics—either its printed dimensions or its image resolution.
-
Choose Paradigm > Epitome Size.
-
To maintain the current ratio of pixel width to pixel pinnacle, select Constrain Proportions. This pick automatically updates the width as you change the meridian.
-
Under Pixel Dimensions, enter values for Width and Height. To enter values as percentages of the current dimensions, choose Percent equally the unit. The new file size for the prototype appears at the top of the Image Size dialog box, with the one-time file size in parentheses.
-
Make sure that Resample Prototype is selected, and choose an interpolation method.
-
If your paradigm has layers with styles applied to them, select Scale Styles to calibration the effects in the resized prototype. This option is available merely if you selected Constrain Proportions.
-
When you finish setting options, clickOK.
For best results when you produce a smaller image, downsample and apply the Unsharp Mask filter. To produce a larger image, rescan the image at a higher resolution.
Change the print dimensions and resolution
When creating an epitome for print media, it'south useful to specify paradigm size in terms of the printed dimensions and the image resolution. These two measurements - referred to every bit the document size - make up one's mind the total pixel count and therefore the file size of the image.
Document size besides determines the base size at which an image is placed into another awarding. You can further dispense the scale of the printed image using the Print control; even so, changes you brand using the Print control affect merely the printed image, not the document size of the image file.
If you turn on resampling for the prototype, y'all can change print dimensions and resolution independently (and change the total number of pixels in the paradigm).If you turn off resampling, y'all can change either the dimensions or the resolution—Photoshop adjusts the other value automatically to preserve the full pixel count.
For the highest print quality, information technology'south recommended to modify the dimensions and resolution first, without resampling. Then resample merely as necessary.
-
Cull Image > Prototype Size.
-
Alter the print dimensions, image resolution, or both:
-
To modify merely the impress dimensions or but the resolution and adjust the total number of pixels in the image proportionately, select Resample Image and then choose an interpolation method.
-
To change the print dimensions and resolution without changing the total number of pixels in the image, deselect Resample Image.
-
-
To maintain the current ratio of epitome width to image height, select Constrain Proportions. This option automatically changes the width every bit y'all change the height.
-
Under Certificate Size, enter new values for the height and width. If desired, choose a new unit of measurement of measurement. For Width, the Columns option uses the width and gutter sizes specified in the Units & Rulers preferences.
-
For Resolution, enter a new value. If desired, cull a new unit.
To restore the initial values displayed in the Paradigm Size dialog box, concord downwardly Alt (Windows) or Pick (MacOS), and click Reset.
What affects file size?
File size depends on the pixel dimensions of an paradigm and the number of layers it contains. Images with more pixels may produce more detail when printed, only they require more than deejay space to shop and may take more time to edit and impress.
Make sure your files are not too large - for large files, reduce the number of layers in the paradigm or change the paradigm size.
You lot can view the file size information for an image at the lesser of the application window.
Source: https://helpx.adobe.com/photoshop/using/image-size-resolution.html
Posted by: robinsonfrogivers38.blogspot.com



0 Response to "How To Check Ppi In Photoshop"
Post a Comment